Hi!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Trust us we hate spamming,
you will get delightful emails
October, 2021
Based on the Oxford dictionary definition, Chatbot, noun. /ˈtʃætbɒt/ /ˈtʃætbɑːt/ a computer program that can hold a conversation with a person, usually over the internet.
The above definition only partially matches our experience of chatbots. We have observed that chatbots do allow us to interact with digital devices as if we are communicating with a real person. They are designed to simulate the way a human would behave with a conversational partner. In many cases, they are designed so sophisticatedly as digital assistants that they learn and evolve to deliver personalization and memory like a real human. Most of us have interacted with a chatbot knowingly or unknowingly; be it a product research assistant, a ticket booking assistant, or a general chit chat assistant like Siri. Presence and advancements in chatbots have shrunk the gap between software and humans. All of this has been achieved because of AI, automated rules, natural language processing (NLP), natural language generation (NLG), etc. However, this was not always the case.

A Bit Of History
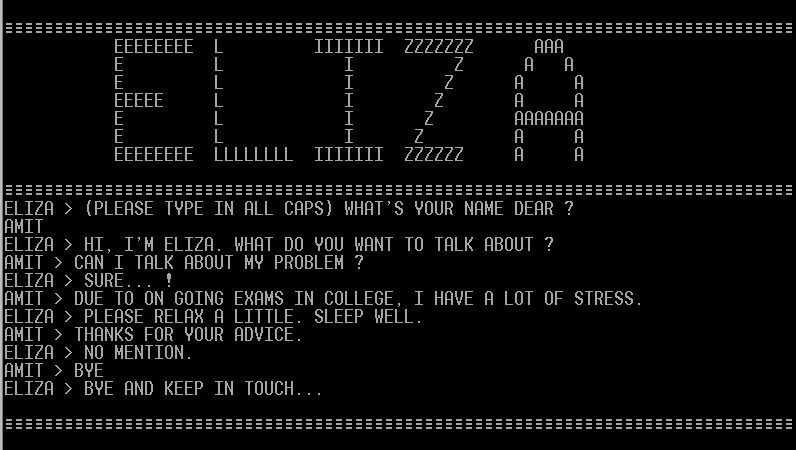
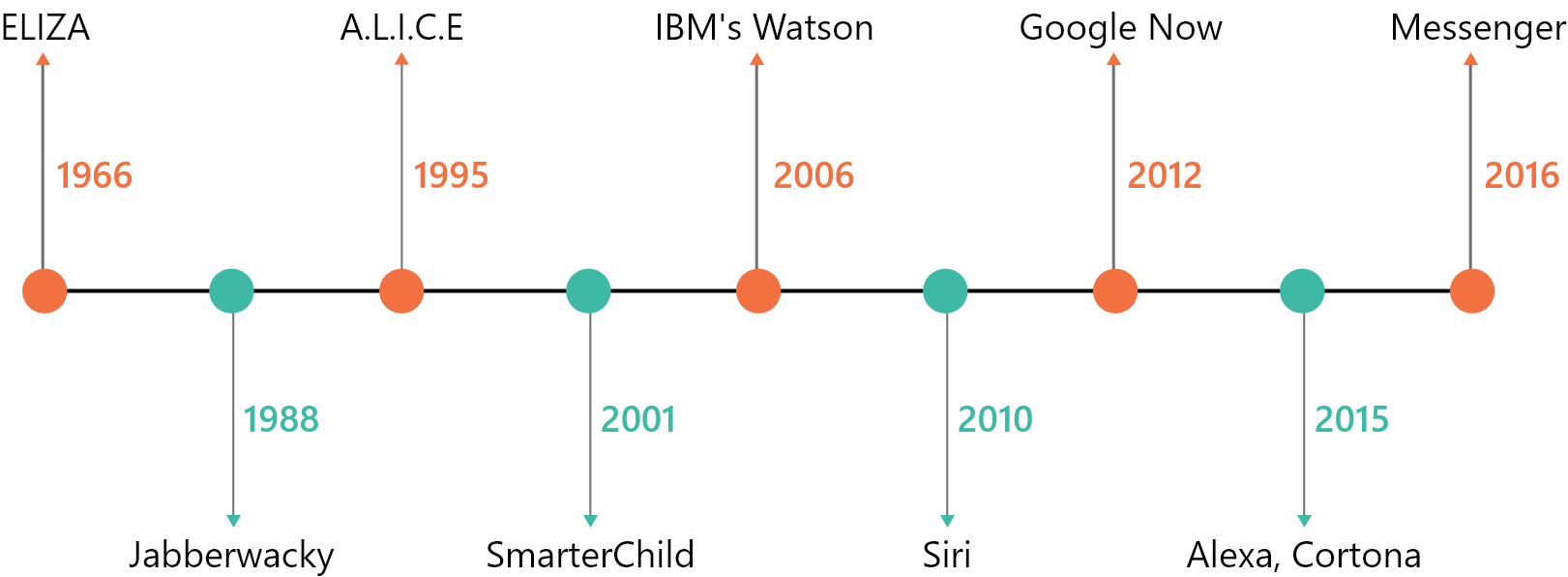
The term ‘Chatbot’ was originally coined by Michael Mauldin (the creator of the first Verbot) in 1994. ELIZA, developed by Joseph Weizenbaum in 1966, is the earliest reference to a chatbot that we can find. It seemed to be able to fool users into believing they were having a conversation with a real human. Based on clues or phrases from inputs, this is still intelligent enough to respond in a meaningful way. However, Weizenbaum himself didn’t claim that ELIZA was intelligent. It still laid down the stream where researchers started working on making software conversant enough with intelligence.
In 1995, Richard Wallace created ALICE. This used XML schema artificial markup language (AIML) to simulate the action of chatting with someone online. In fact, this chatbot was designed with the persona of a young woman who could tell you interesting facts about herself, and other details. While it won the Loebner prize thrice, it failed to pass the Turing test.
Before the launch of Siri and other conversational chatbots, we saw many other chatbots. Who can forget JARVIS (Just A Rather Very Intelligent System), an assistant to Mr. Tony Stark, Iron Man (2008). Between 2010-2015, chatbots started becoming more intelligent and conversational. This was the time when Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, and Cortana started coming up with very impressive ways of communicating with machines. The AI boom had started around that time and was impacting the way of working in all aspects of life.
The Impact of AI
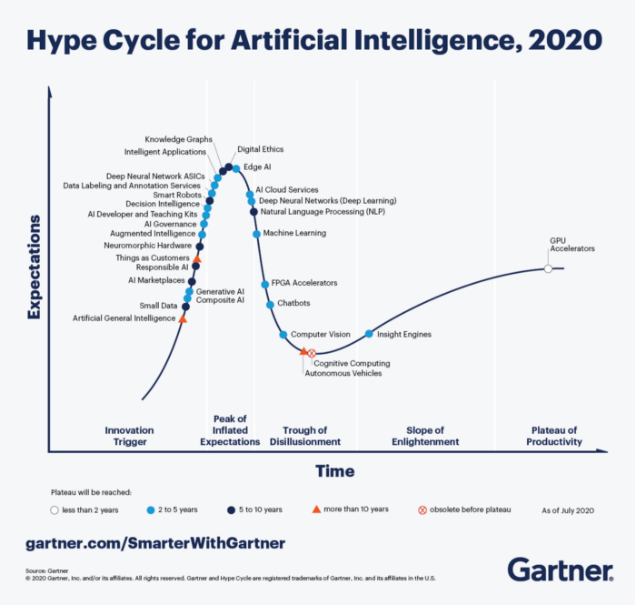
The AI boom started picking up in 2016 onwards, and since then we have seen very fast changes in chatbots. The position of chatbots in Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence Report has changed drastically since 2018. In 2019, it was at the peak of inflated expectations, and by 2020, it reached a state of disillusionment. This trend fits well with AI and ML technologies.
Even though chatbots started with rule-based automated responses, AI gave them a different dimension. By the middle of 2019, it has evolved from a “Chatbot” to a “Virtual Assistant”. With the evolution of Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG), virtual assistants have started to offer very personalized and more human-like interactions.
Gone are the days when assistants were used for FAQ purposes only. Such assistants were known to provide quick responses to simple questions. Though it is a very common use case even today, its implementation and customer experience have changed much beyond getting an answer to a simple query. Menu-based assistants are also very specific to a few use cases only, e.g. restaurants or ticket booking assistants. Then came Contextual Assistants. This is where context matters for understanding and responding to different unexpected inputs. Users can freely type in here, and the assistant fully understands and responds. Such a conversation is possible only due to advancements in the field of AI.
Now we are working on Personalized Assistants that can understand and behave like humans. It will know the user based on previous interactions. It will also learn when to get in touch with a user and can proactively reach out to a user based on their contexts. It has long term memory of previous conversations and works with augmented responses. Such assistants can not only be used in typical use case scenarios, but can also be effectively used for general-purpose conversation bots as well.
Are Chatbots Bad?
There have been discussions on various forums over the legitimate or malicious purpose of their usage. Just like everything, there have been cases where chatbots have gone wrong. How can we forget the history of Tay, the chatbot designed by Microsoft in 2016? It couldn’t stand for more than 24 hours due to various abusive internet trolls. This was one of the very early examples of AI getting manipulated. Nowadays, various AI models are used to classify abusive and hateful speeches. These models are used to reduce the tampering of the core response models of assistants.
Apart from instances where assistants went rogue, there have been concerns about realized gains in their usage. Customer satisfaction has been the driving force of any virtual assistant for a long time. Customer experience was not up to the mark during the initial days. It was mainly due to rule-based assistants. Due to the advancement in AI, assistants have started behaving very much like humans and have also gained the empathy of customers. Ongoing research in AI models/transformers has dramatically diminished or even eliminated the need for historical data.
Humans are conversational entities, and we feel very comfortable when we speak to someone who can speak our language and in our way. If virtual assistants can do that, along with analyzing information and decision-making abilities, then they will be an integral part of our lives for sure.